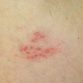
Hives are a quite prevalent skin condition among children. They appear as red or white, inflamed, and itchy bumps on the skin. Hives typically only persist for only a few hours or a few days at the most, but in certain chronic cases, they may last longer, possibly for up to a few weeks. Hives usually develop when the body secretes the substance known as histamine in response to contact with an allergen or even simply temperature changes, infections, and stress. If your child is suffering from hives, you can either consult his or her doctor to get a prescription or try some at-home treatments.
Pay your child’s doctor a visit first
It is important to understand more about hives since children are prone to them. Hives may appear on small sections of your child’s body or their entire body, and being knowledgeable about their appearance may guide you through pinpointing the root cause. Hives that form in small parts of the body are typically a result of physical contact with allergens or irritants such as pollen, foods, animal dander, or plants. When hives affect the whole body, this may also be due to a viral infection.
Understand the triggers of hives
Your child may form hives due to a host of various reasons. Understanding the primary triggers involved in the development of hives can be helpful in treating it effectively at home. The most common hives triggers include:
– Foods like nuts, dairy, or shellfish; hives caused by food allergies typically disappear in several hours
– Certain medications like
– Animal dander may cause hives
– Allergies to plants and pollen
– Insect bites such as bee stings or mosquito bites
– Hives may be induced by anxiety
– Too much sun exposure or sudden temperature changes can cause hives
– Contact with products containing harsh chemicals can also result in hives
– Viral infections such as the common cold or hepatitis can also trigger the development of hives
Consult your child’s pediatrician about hives
It is a good idea to pay your child’s pediatrician a visit to pinpoint the cause of your child’s hives, especially if the hives do not go away in 7-10 days or if your child begins to experience severe discomfort. When you are unsure as to what may be causing your child to break out in hives or unsure of how to treat it, it is crucial to take him or her to their pediatrician. Their pediatrician can put your child on medications, recommend ointments, or prescribe other therapies to relieve symptoms.
Your child may need medical tests
If your child’s pediatrician cannot pinpoint the root cause of the hives, they may order a variety of tests to rule out certain conditions that may be causing hives. This is not only imperative with regards to nailing down the cause but also in finding the ideal treatment approach to eliminate symptoms.
Addressing an underlying disease
If your child’s doctor concludes that your child has developed hives due to an underlying disease, they will likely put together a treatment plan for the condition that is the cause of the hives to relieve the bumps and itching. Research shows that nipping the underlying condition in the bud is often more fruitful in easing hives than directly treating them.
Keep your child away from triggers
Hives may happen due to contact or exposure to an allergen or irritant such as certain foods, medications, self-care/hygiene products, too much exposure to sunlight, stress, and insect bites. Identifying the triggers that result in your child breaking out in hives can ultimately help you keep them away them to prevent outbreaks.
Featured Image: Depositphotos/© geengraphy