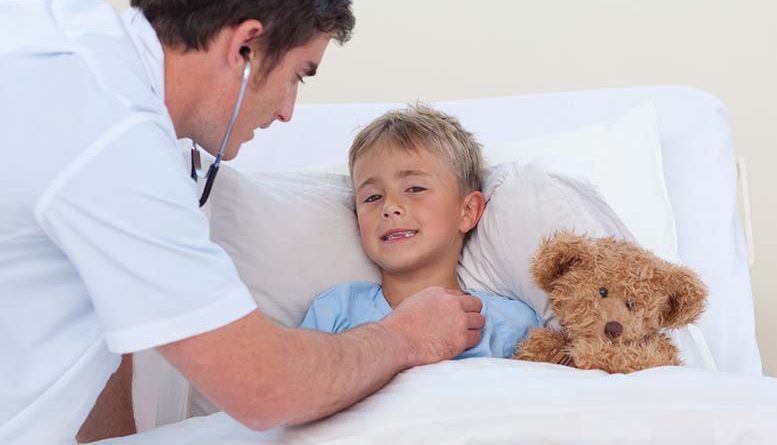
Pneumonia can be a severe and potentially life-threatening condition. The cause of pneumonia is usually a bacterial or viral infection of the lungs, both of which can be quite dangerous. If you suspect your child is exhibiting symptoms of pneumonia, it is essential to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia symptoms differ depending on the age of a child as well as the root cause of the infection. For babies and infants over one month of age, symptoms are comparable to those experienced by adults.
Bacterial pneumonia symptoms are usually a persistent cough that is coupled with green or brownish mucus production, high fever accompanied by chills and sweats, fast heart rate, feeling fatigued, nausea, and diarrhea. Viral pneumonia symptoms may include a high fever, persistent cough without mucus, and breathlessness. In babies under the age of one month, the symptoms may consist of fever, loss of energy, feeding difficulties, and snorting.
Diagnosing Pneumonia
In diagnosing pneumonia among children, there exists a variety of methods and approaches. Your child’s doctor may check your child’s heartbeat by evaluating their breathing over the course of 60 seconds. There are also other diseases that bring on symptoms akin to those of pneumonia such as tuberculosis and bronchitis, and these conditions have different treatments. Your child’s doctor may also order blood tests, take a mucus sample to check for bacteria, or need an imaging test to reach a conclusive diagnosis.
Pneumonia Treatment Options
When the cause of pneumonia is a bacterial infection, the treatment method usually involves antibiotics. However, antibiotics are not preferred when pneumonia is due to a viral infection. Viral pneumonia is best left to take its course and improve on its own without interfering unnecessarily. Following a diagnosis, your doctor will determine whether your child needs to be hospitalized or looked after at home. If he or she does not need to be hospitalized, your child will need close monitoring and will need to be provided with the treatments recommended by his or her physician as instructed.
Preventing Pneumonia
While it is impossible to keep pneumonia at bay at all times, vaccinations can greatly lower the risk of infection. Children who are at an increased risk of catching pneumonia such as those who were born prematurely or have an existing chronic condition may be provided with preventative treatments if needed.
Featured Image: Depositphotos/© Wavebreakmedia