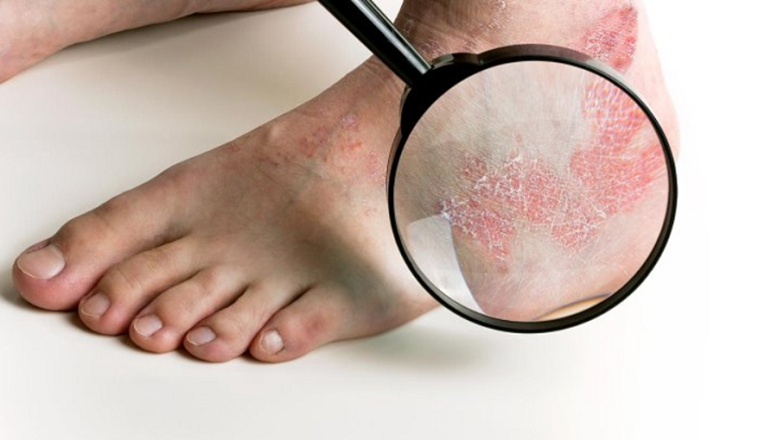
Eczema, also referred to as atopic dermatitis, is a condition that results in red, dry, itchy, and flaky patches of skin. Eczema is chronic and causes recurrent outbreaks with periods of remission.
Although eczema still cannot be cured, preventing flare-ups and relieving symptoms such as itching is possible with the availability of numerous treatment options. Avoiding products that contain harsh chemicals such as soaps and cosmetics, finding an ointment or medicated cream, and daily moisturizing goes a long way in controlling symptoms and keeping flare-ups at bay.
Overall, primary eczema symptoms consist of dry, itchy, and flaky patches of skin, which may become itchier at night; these affected areas of skin may also form small red bumps that can get pus-filled and get crusty with scratching. Scratching may also cause the lesions to become tender and more inflamed. Eczema patches most commonly appear on the upper chest, neck, hands, wrists, feet, ankles, and in the folds of the knees and elbows.
Eczema Complications
Hay Fever and Asthma
The development of eczema can herald both allergic rhinitis (hay fever) and asthma. Many children with eczema get diagnosed with hay fever and asthma before they hit puberty.
Neurodermatitis
A skin disease known as neurodermatitis begins with a small area of itchy skin where scratching it causes it become much itchier. Over time, scratching may become a force of habit. Neurodermatitis can result in the hardening and discoloration of the affected area.
Infections
Continuous scratching that damages the skin can result in open sores and fissures, which make the skin more susceptible to viral and bacterial infections.
Irritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis
A condition that most commonly affects the hands; this complication is especially a concern for those whose hands are frequently exposed to water, soaps, and cleaning supplies such as detergents. Additionally, people with eczema typically tend to develop allergic contact dermatitis as well.
Sleep Difficulties
The constant itching and urge to scratch may get in the way of a good night’s sleep, leading to a decline in the quality of sleep.
Preventing Eczema
Here are some tips that are effective in preventing periods of flare-ups and lessening the dryness bathing may cause:
Make it a habit to moisturize two times every day
Various types of moisturizing creams and lotions can help you in retaining enough moisture in your skin. Selecting the right product is key.
Pinpoint your triggers
If you know the triggers that aggravate your condition such as stress, excess weight, sweat, harsh soaps, cleaning products, and allergens like pollen, you can successfully keep away from your triggers to prevent outbreaks.
Shorten your shower/bath time
Make sure not to take a shower or bath longer than 15 minutes, and avoid using hot water. Warm water is your friend.
Try a bleach bath
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, a 10-minute bleach bath twice a week can be effective in preventing flare-ups. You need 1/2 cup non-concentrated, household bleach for a standard 40-gallon tub of warm water. Do not immerse your head in the water.
Avoid harsh soaps
Try to choose mild soaps that contain little to no harsh chemicals; soaps with fragrance and antibacterials can dry out the skin more.
Featured Image: Twitter