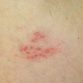
Hives, also known as urticaria, are characterized by red, swollen bumps or plaques of varied sizes that can form anywhere on the skin typically in reaction to contact with allergens. However, in some cases, the cause of hives is unknown. Although most cases of hives improve over the course of 24 hours, there are long-lasting types that can persist for months or years.
The good news is that relieving hives does not cause much difficulty. Here is an overview of treatment options determined by the severity of the hives.
Treatment of Mild Hives
When a person experiences a case of mild hives, they may not require treatment given that they will improve on their own, usually in a few hours. However, using an antihistamine cream can speed up the healing process and alleviate inflammation and itching.
Treatment of Moderate Hives
In cases of hives with moderate severity, your doctor may prescribe you antihistamine medicines. However, keep in mind that these drugs tend to have drowsiness as a side effect. Additionally, your physician may also put you on corticosteroid medications which are highly effective in alleviating inflammation, irritation, and itching. Prolonged use of corticosteroids must be avoided, however, as these are potent drugs that can cause some adverse side effects in the long run.
If these treatment methods prove to be ineffective, you may be prescribed immunosuppressants to control the immune system response responsible for the skin reaction.
Treatment of Severe Hives
When an individual has a case of severe hives, the condition extends beyond just bumps on the skin and may cause swelling in the throat, leading to breathing or swallowing difficulties. Hence, if you experience any of these symptoms with hives, it is crucial to see a doctor as soon as possible. The standard treatment approach to severe hives is the use of epinephrine, which prevents any life-threatening complications.
People who have chronic hives may need to get a prescription for an (epinephrine injection device) to keep on their person in case of an emergency. Regardless of whether one has an or not, however, it is still important to seek medical attention if you experience a severe breakout.
Prevention of Hives
Keeping clear of personal triggers is the only surefire way to keep hives at bay. Some of the most common hives triggers are:
– Food allergies such as nuts and shellfish
– Allergies to medications like or NSAIDs such as ibuprofen
– Certain clothing material
– Insect Bites
– Sudden temperature changes
– Increased body temperature due to physical activity
– Allergens such as animal dander, latex, or pollen
– Irritant plants like poison ivy
Featured Image: Depositphotos/© IgorVetushko